Diabetes and Amputation: Preventive Measures and Foot Care
Foot ulcers and the risk of amputation are serious concerns for individuals living with diabetes. While not everyone with diabetes will require amputation, there are two common conditions associated with the disease that may lead to this outcome: peripheral artery disease (PAD) and diabetic neuropathy. This article delves into the connection between diabetes and amputation, shedding light on preventive measures and highlighting the importance of regular foot care.
Let’s understand more about the link between diabetes and amputation and how you can prevent it.
How Diabetes May Lead to Amputation:
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a circulatory disorder characterized by narrowed arteries, which can result in reduced blood supply to the limbs, primarily the legs. Insufficient blood circulation increases the likelihood of developing open ulcers and infections. When healing is compromised due to compromised blood flow, the risk of severe complications escalates.
Diabetic Neuropathy, on the other hand, is a condition that damages the nerves, leading to pain and discomfort. Elevated blood sugar levels can cause damage to the nerves and blood vessels throughout the body, including the feet and legs. Nerve damage can result in a loss of sensation, making it difficult to detect symptoms such as ulcers, infections, or injuries.
Both PAD and diabetic neuropathy significantly elevate the risk of severe infection or tissue death (gangrene). In extreme cases, amputation may be the only viable option to control the spread of gangrene and prevent further complications.
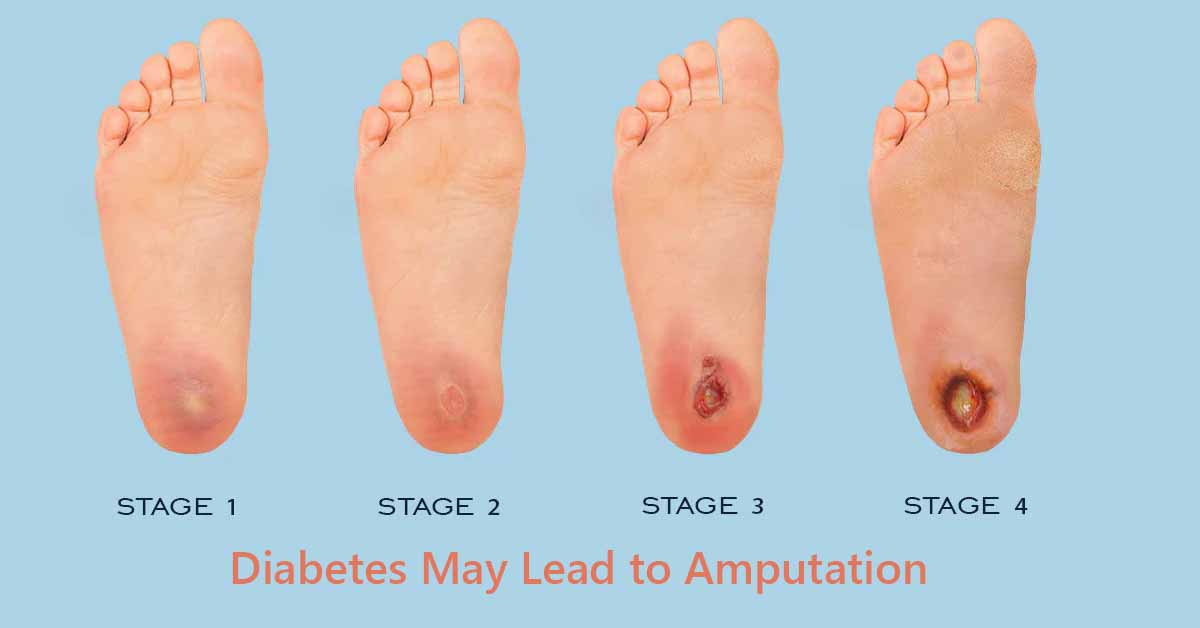
Preventing Amputation:
For individuals living with diabetes, taking diligent care of their feet is crucial in minimizing the risk of amputation. Additionally, managing other health conditions, such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol, plays a vital role in mitigating complications.
Here are some preventive measures to follow::
Regular Foot Inspection: Check your feet daily, examining even the spaces between your toes. Look for any signs of concern, such as sores, cuts, blisters, thick calluses, redness, cracks, warm spots, discoloration, pain, bleeding, foul odor, or slow-healing sores.
Proper Foot Care: Take the following actions to care for your feet effectively:
- Wear dry socks to maintain foot hygiene and prevent moisture buildup.
- Stimulate blood flow by wiggling your toes regularly.
- Ensure to wash your feet every day using a gentle soap and warm water.
- Avoid removing calluses at home; seek professional assistance instead.
- Trim your toenails straight across and file the edges to avoid ingrown toenails.
- Avoid walking barefoot to prevent injuries.
- Wear appropriate shoes that provide ample support, protection, and proper fit.
- Different colors, an indication of a problem with blood supply
- Schedule regular foot examinations with a healthcare professional or a podiatrist.
Seek Medical Attention: If you are unable to inspect your feet, ask a family member or caregiver to help. Report any abnormalities or concerns to your doctor immediately.
Lifestyle Choices: Quitting smoking is essential as it damages blood vessels, restricts blood flow to the feet, and increases the risk of amputation. Engaging in daily exercise not only aids in controlling diabetes but also improves blood circulation. Managing stress, taking medications as prescribed, following a well-balanced diet, and limiting the consumption of sugary foods and drinks are also essential steps in managing diabetes and its associated risks.
Conclusion:
Managing diabetes and preventing the need for amputation is achievable through consistent foot care, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, and effectively managing other risk factors. Remaining vigilant and promptly seeking medical attention for any abnormalities or concerns is crucial. By implementing these small yet significant measures, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce the likelihood of amputation and enhance their overall well-being.